Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
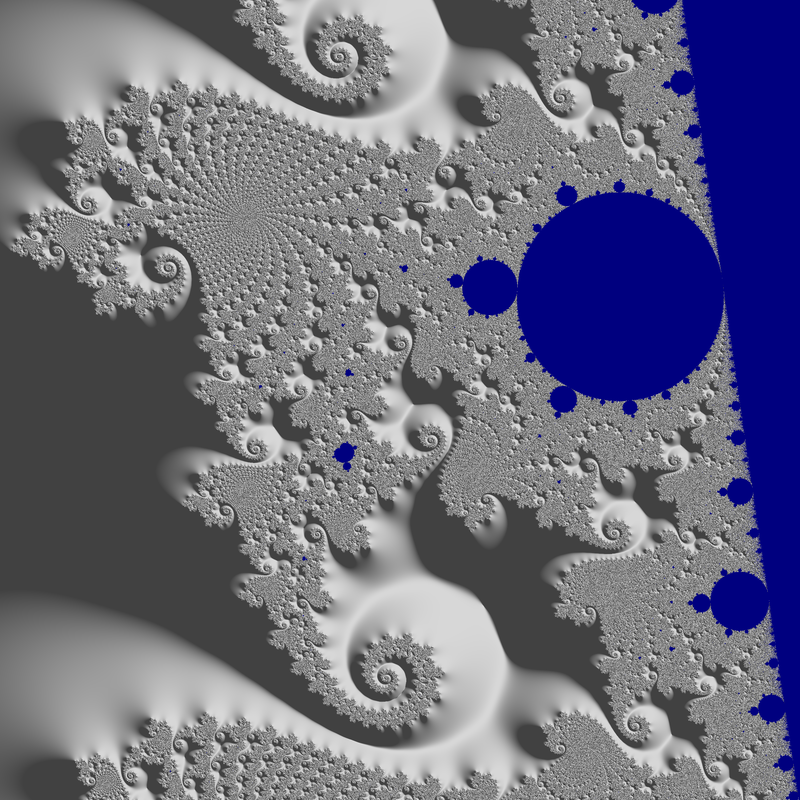
04 - Seahorse shaded example
This example shows how to create a normal map layer, and link it to a base color layer to enable scene lighting. Here a fully grey background is used, and the normal map layer is based on “Milnor estimator”.
The location is a shallow one in the main Seahorse valley.
Reference:
fractalshades.models.Mandelbrot
import os
import numpy as np
import fractalshades as fs
import fractalshades.models as fsm
import fractalshades.colors as fscolors
from fractalshades.postproc import (
Postproc_batch,
Continuous_iter_pp,
DEM_normal_pp,
Raw_pp,
)
from fractalshades.colors.layers import (
Color_layer,
Bool_layer,
Normal_map_layer,
Blinn_lighting
)
def plot(plot_dir):
"""
Using lighting : a shallow zoom in the Seahorses valley
Coloring based on continuous iteration + lighting with a normal maps from
distance estimation method
"""
fs.settings.enable_multithreading = True
fs.settings.log_directory = os.path.join(plot_dir, "log")
fs.set_log_handlers(verbosity="debug @ console + log")
# Define the parameters for this calculation
x = -0.746223962861
y = -0.0959468433527
dx = 0.00745
nx = 2400
calc_name="mandelbrot"
colormap = fscolors.Fractal_colormap(
colors=[[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
[0.5, 0.5, 0.5]],
kinds=['Lab'],
grad_npts=[2],
grad_funcs=['x'],
extent='mirror'
)
# Run the calculation
f = fsm.Mandelbrot(plot_dir)
f.zoom(x=x, y=y, dx=dx, nx=nx, xy_ratio=1.0,
theta_deg=0., projection=fs.projection.Cartesian())
f.calc_std_div(
calc_name=calc_name,
subset=None,
max_iter=25000,
M_divergence=100.,
epsilon_stationnary= 0.01,
calc_d2zndc2=True
)
# Plot the image
pp = Postproc_batch(f, calc_name)
pp.add_postproc("cont_iter", Continuous_iter_pp())
pp.add_postproc("interior", Raw_pp("stop_reason", func="x != 1."))
pp.add_postproc("DEM_map", DEM_normal_pp(kind="Milnor"))
plotter = fs.Fractal_plotter(pp)
plotter.add_layer(Bool_layer("interior", output=False))
plotter.add_layer(Normal_map_layer("DEM_map", max_slope=60, output=False))
plotter.add_layer(Color_layer(
"cont_iter",
func="np.log(x)",
colormap=colormap,
probes_z=[1., 2.],
output=True
))
plotter["cont_iter"].set_mask(plotter["interior"], mask_color=(0., 0., 0.5))
plotter["DEM_map"].set_mask(plotter["interior"], mask_color=(0., 0., 0.))
# This is where we define the lighting (here 3 ccolored light sources)
# and apply the shading
light = Blinn_lighting(0.25, np.array([1., 1., 1.]))
light.add_light_source(
k_diffuse=3.0,
k_specular=0.1,
shininess=400.,
polar_angle=45.,
azimuth_angle=40.,
color=np.array([1.0, 1.0, 1.0])
)
plotter["cont_iter"].shade(plotter["DEM_map"], light)
plotter.plot()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Some magic to get the directory for plotting: with a name that matches
# the file or a temporary dir if we are building the documentation
try:
realpath = os.path.realpath(__file__)
plot_dir = os.path.splitext(realpath)[0]
plot(plot_dir)
except NameError:
import tempfile
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as plot_dir:
fs.utils.exec_no_output(plot, plot_dir)
Total running time of the script: ( 1 minutes 23.717 seconds)